Fries Rearrangement: Mechanism, Applications, and Key Facts
Fries Rearrangement
The fries rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction of a phenolic ester to a hydroxyl aryl ketone by using Lewis as catalysts.
The Fries rearrangement, named for the German chemist Karl Theophil Fries, is a rearrangement reaction of a phenolic ester to a hydroxy aryl ketone by catalysis o
The reaction is a ortho and para selective and one of the two product can be favoured by changing the reaction condition, such as Temperature and solvent.
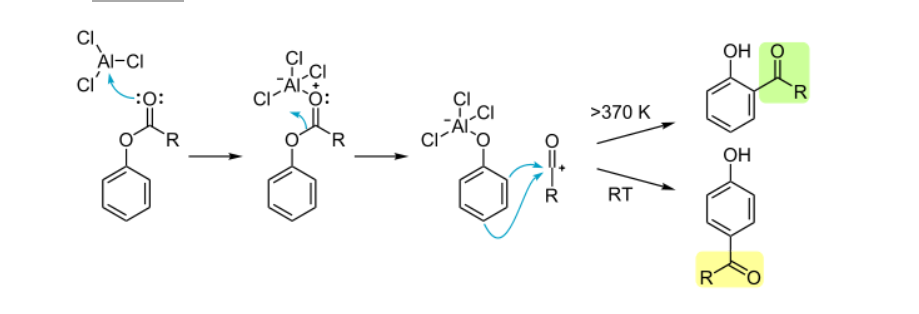
The Fries rearrangement is a classic organic reaction that converts phenyl esters into hydroxyaryl ketones using a Lewis acid catalyst (typically aluminum chloride, AlCl₃). This reaction is widely used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and UV stabilizers.
Mechanism of Fries Rearrangement
Step 1: Lewis Acid Coordination
AlCl₃ binds to the ester carbonyl oxygen, activating the carbonyl carbon.
Step 2: Acylium Ion Formation
The C-O bond cleaves, generating reactive species
Step 3: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
The acylium ion attacks the aromatic ring:
- Ortho attack (favored at >100°C)
- Para attack (favored at 25°C):
Step 4: Rearomatization
Proton loss yields the final product.

How To Preparation and Standardization of 0.1N KMnO4 Solution?
Determination of Free Fatty Acids (FFA)
Why Does Rainwater Conduct Electricity While Distilled Water Doesn’t? (Objective Questions & Answers)
What is the name of the compound: NH3?
Naphthalene, Structure and Reactivity & Other Names Of Naphthalene
Applications of Fries Rearrangement
1. Synthesis of Hydroxyaryl Ketones
- Fries rearrangement is a direct route to compounds like hydroxyacetophenones, which are precursors in pharmaceuticals, perfumes, and dyes.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Used in the synthesis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as paracetamol analogs.
- Helps in preparing intermediates for various antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents.
3. Production of UV Stabilizers and Antioxidants
- Many hydroxyaryl ketones derived from Fries rearrangement are used in manufacturing UV absorbers and antioxidants in plastics and rubbers.
4. Perfume Industry
- Aromatic ketones like 4-hydroxyacetophenone are important fragrance ingredients or used in the synthesis of aroma compounds.
5. Synthesis of Agricultural Chemicals
- Used to create intermediates in the manufacture of pesticides and herbicides.
6. Materials Chemistry
- Starting materials for the synthesis of high-performance polymers, especially where aromatic ketones provide thermal and mechanical stability.
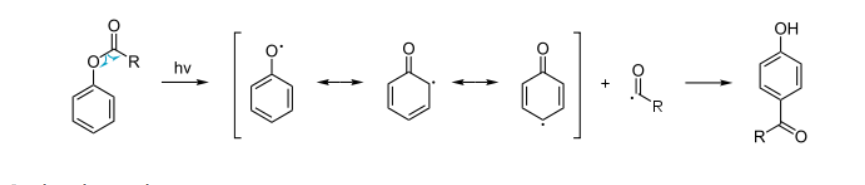
Photo-Fries rearrangement
The Photo-Fries Rearrangement is a photochemical version of the Fries rearrangement, in which aryl esters are rearranged under UV light to give hydroxyaryl ketones (ortho- and para-isomers). Unlike the classical Fries rearrangement that uses Lewis acids, the photo-Fries rearrangement proceeds through radical intermediates.
- 0.1 normal NaOH solution
- 0.1N NaOH solution for lab experiments
- 0.1N NaOH solution kaise banaye
- 10th exam
- Acid base and Salt class 10
- Acid base and salt note
- Acid base salt note pdf
- Acid-base titration
- Acids and Bases Class 10 MCQs
- Acids Bases and Salts MCQs with Answers
- Acids Bases and Salts Objective Questions
- All Named Reaction In PDF
- allotropes of carbon
- and mode of action. Below is a detailed classification:
- and Uses
- Applications
- Applications and Uses of Copper
- Applications of Fries Rearrangement
- Arrhenius theory
- biochemistry lab experiments
- board exam
- Boric acid
- Boric Acid (H2BO3 ) 4% preparation
- Boric Acid (H2BO3 ) practical
- Boric Acid Solution
- Brain Person Takes Drugs
- bseb
- BSEB Class 10 Chemistry Objective
- by sadre alam electronic configuration elements
- carbon and its compounds
- carbon and its compounds class 10
- carbon bonding and structure
- carbon chemistry for student
- carbon chemistry note
- carbon compound reaction
- Catalyst-Driven Reactions: Mechanisms and Examples
- Catalysts can be classified into several categories based on their nature
- Catalysts in Chemistry: Types
- cbse chemistry mcqs
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry MCQs
- CBSE Class 10 Science
- Chemical normality
- chemical reactions of chlorine
- Chemical Structure of Citral
- Chemistry class questions with answers
- Chemistry experiments
- chemistry mcq questions
- chemistry note
- Chemistry practical
- chemistry table
- chemsadre
- chemsadre.com
- chlorine
- chlorine chemistry explanation
- chlorine class 10 notes
- chlorine in periodic table table
- Citral of Isolation
- Class 10 Board Exam Science question
- class 10 chemistry
- Class 10 Chemistry Board Exam
- Class 10 Chemistry MCQs question with answer
- Class 10 science chapter Metals and Non-Metals
- Class 10th chemistry acid base and salt note
- Classe10 MCQs
- copper position in pt
- Covalency vs Valency
- Cured Or Prevented
- deffination of metal
- defination of chemistry
- Derivation of the Schrödinger Equation
- diamond structure and uses
- DMAB (Dimethyl Amino Benzaldehyde).
- Drug Addiction
- Electronic Configurations of All Elements
- eqation
- Experiment of Boric Acid
- Fat Soluble Vitamins
- find noble gas periodic table
- Fries Rearrangement
- Functions
- graphite properties
- Handwritten chemistry notes
- HCl solution preparation
- How To Find Valency Videos
- how to learn chemistry periodic table
- how to learn Electronic Configurations of All Elements
- How To Learn Periodic Table Like a Memory Rockstar
- Importance of Chemistry in Our World
- Important Shorts Notes
- Indicators MCQs Chemistry
- industrial lab test
- inorganic carbon compounds
- Inorganic chemistry notes
- Interpretation of the Wave Function
- iodometric titration procedure
- Isoprene Rule
- Laboratory me NaOH solution kaise banaye
- Limitations of Ohm’s Law
- Main Branches of Chemistry
- matrik exam
- mcqs with answers chemistry
- Mechanism of Fries Rearrangement
- Mention any five importance of pH in our daily life?
- Metals and Non Metals Class 10 Notes PDF download
- Metals and Non Metals Class 10 Notes Prashant Sir 1
- Metals and Non Metals Class 10 Notes self study
- Metals and Non Metals Notes PDF
- Metals and Non-Metals Class 10
- Metals And Non-Metals Complete Chapter Notes With Examples
- Name reaction pdf
- NaOH solution preparation
- NaOH solution safety precautions
- NCERT class 10 metal and Non-Metals
- NEET chemistry notes JEE Main Tin properties
- normality of sodium thiosulfate
- occurrence of chloprine
- Ohm’s Law Definition
- Ores of Cupper
- ores of phosphorus
- organic chemistry basic
- organized reference covering definitions
- Other economic importance of Ammonia :
- Our Daily life uses chemistry
- p block group
- periodic table
- pH Scale Class 10
- phase
- Phosphorus (P) is a highly reactive non-metal and is never found in its free state in nature.
- Phosphorus (P) Position In the Periodic Table
- Photo-Fries rearrangement
- physical/chemical properties
- postion of chlorine
- Preparation of 0.2N HCl
- Preparation of Boric Acid
- preparation of phosphorus
- Riemer-teiman reaction pdf
- s block group
- sadre alam
- Salts Chemistry Class 10
- Santonin Source
- SCHRODINGER WAVE EQUATION
- SCHRODINGER WAVE EQUATION & DERIVATION
- short exam question and answer
- Sodium hydroxide ke solution ki taiyari
- Sodium thiosulfate normality calculation
- Sources of vitamin
- Special Isoprene Rule and Violations Of Isoprene Reule
- spot test urea
- Structure and synthesis
- Structure of citral
- The Importance of the Periodic Table in Chemistry
- The name of the Compound NH3 is Ammonia gas .
- The number of covalent bonds an atom can form by sharing electrons.
- The Schrödinger Wave Equation: Fundamental Principles and Mathematical Formulation"
- Tin chemical properties
- Tin compounds for exams
- Tin Sn notes PDF
- Tin uses in chemistry
- tirck to learn chemistry periodic table
- Titration of HCl
- trick to learn periodic table
- types of catalysts
- urea positve test
- urea spot DMAB (Dimethyl Amino Benzaldehyde).
- urea spot test
- urea spot test principle
- urea spot test procedure
- use opf citral
- uses and Structure
- Uses Complete Note of copper
- uses of chlorine
- Valency
- Verification of Ohm’s Law
- Vitamin
- vitamin all chemical name
- Vitamin Deficiency
- vitamin name
- vitamin note for exam
- vitamin Sample Questions
- vitamin source
- Water Soluble Vitamins
- What happens to the brain when a person takes drugs?
- What is Chemistry
- What Is drug addiction?
- What is isoprene rule?
- What is the covalency
- What is the name of the compound: NH3?
- Whereas Rainwater Does
- Why Distilled Water Does Not Conduct Electricity
- Why It Doesn't Conduct Electricity
- ऊर्जा का उच्चतम स्रोत किसे कहते हैं
- क्लास 8
- ग्रह क्यों नहीं टिमटिमाते दिखाई पड़ते हैं?
- ग्रह क्यों नहीं टिमटिमाते?
- डायनमो किसे कहते हैं?
- दूर दृष्टि (Dur Drishti / Hypermetropia) क्या है
- विद्युत बल्ब में निष्क्रिय गैस क्यों भरी जाती है?
- सूक्ष्मजीव: हमारे दोस्त या दुश्मन? 🤔 क्लास 8 के बच्चों के लिए सुपर आसान हिंदी नोट्स!
- हिंदी नोट्स








1 comment