Inorganic Chemistry
Acid base and Salt class 10, Acid base and salt note, Acid base salt note pdf, Arrhenius theory, Class 10th chemistry acid base and salt note, Mention any five importance of pH in our daily life?, organized reference covering definitions, physical/chemical properties
sadrealam.umg@gmail.com
1 Comments
Chemistry Complete Acid Base Salt and pH Scale With Examples
Acid
An acid is a substance whose aqueous solution is sour in taste and reacts with metal to liberate hydrogen gas.
The word acid is derived from the Latin word acitak, meaning sour.
- A compound that release H+ ions.
- Turning blue Litmus Red.
- Sour taste.
Base
Base is a substance whose aqueous solution is bitter in taste and neutralises acids to form salts.
- A compound that Produces OH- inos.
- Turning red litmus blue.
- Bitter taste and soapy.
Salt
- Generally Neutral in Solution.
- Ionic product from Acid Base Neutralization.
- The most Common Example NaCl and table Salt.
Different Between Acid And Base
| Acid | Base |
|---|---|
| pH Value Less than 7 | pH Value Greater than 7 |
| Turn Blue Litmus paper is Red | Turn Red Litmus paper is Blue |
| Ions Released H+ ( Hydrogen Ions). | Ions Released OH– ( Hydrogen Ions). |
| Acid Teste Sour | Base teste Bitter |
| Acid Example- HCL, H2SO4, NH3 | Base Example- NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2 |
| Acid Alwayse Proton Donor. | Base alwase Proton acceptor. |
Indicators
- Find the color solution is Acid, Base and Neutral to Show Chemical Reaction.
- Signal the endpoint of a chemical reaction (Acid/Base)
- Response to pH changes
Type Of Indicators
pH Indicators
Litmus Paper-Turns Blue in Basic and Red in Acidic.
Methyl Orange- Acidic medium Red/Pink and Basic medium Yellow.
Phenolphthalein- Basic Solution in Pink Show and Acidic Solution colorless (No Any Color Show).
Natural Indicators
Turmeric-
Red Cabbage-
Types of acids based on strength
There are two types of acids based on their strength
Strong acids– Acids which are completely dissolved in water are called strong acids, such as HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, etc.
Weak acids- Weak acids and acids that dissolve in water and become only partially ionic are called weak acids. Example: H2CO3, H3BO3 CH3COOH etc.
Boric acid H3BO3 is also a weak acid which is used as an antiacid.
Boric acid partially ions in water and forms very few hydrogen ions, hence its electrical conductivity is also low.
The most important property of an acid is that it neutralizes a base. And the most important property of a base is that it neutralizes an acid.
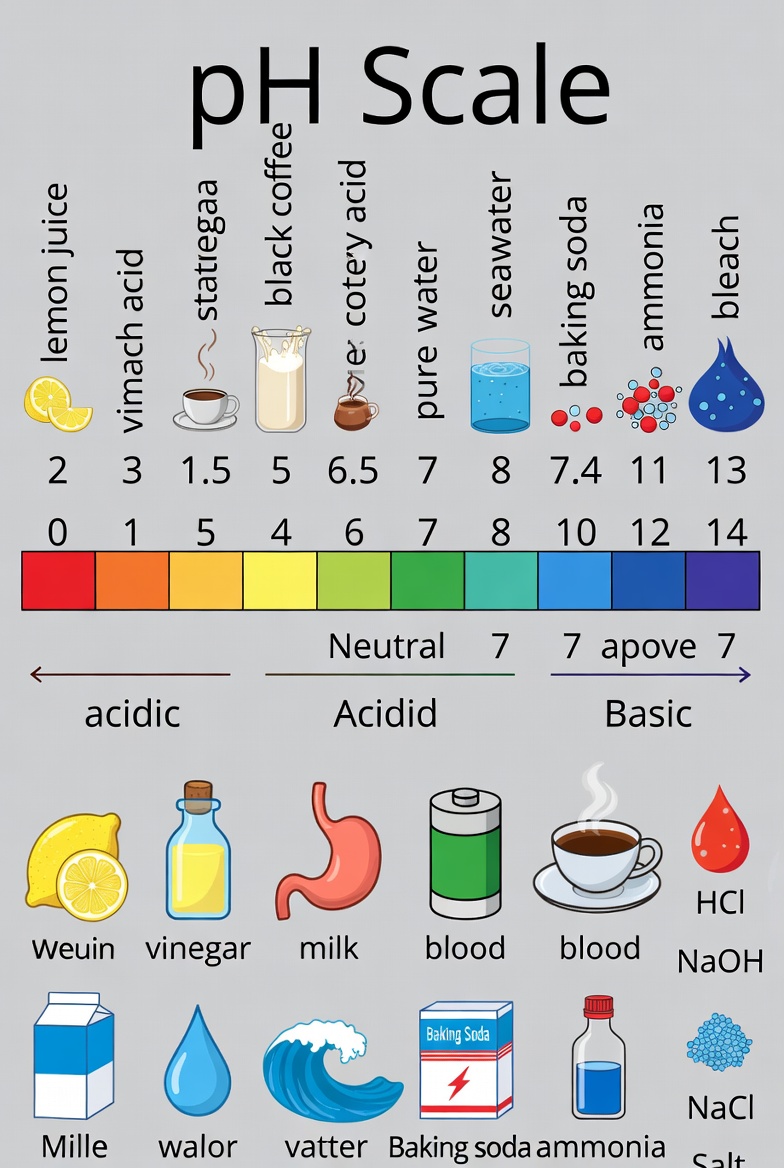
pH Scale
The negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is called the pH of a solution.
pH Full Name – Power Of Hydrogen
The pH value ranges from 0 to 14.
pH=7 Neutra
pH< 7 Acidic
pH>7 Basic
The father of pH- Soren Peter Lauritz Sorensen (S.P.L Sorensen)
| Substance | pH |
|---|---|
| Green Mango | 3.4-4.8 |
| Stomach Acid | 1.5-3.5 |
| Urine | 4.5-8.0 |
| Drinking Water | 6.5-8.5 |
| Blood | 7.35-7.45 |
| Rain Water | 5.6 |
| Sirca (Vinegar) | 2.5-3.5 |
| Tomato Juice | 4.0-4.5 |
| Grape Juice | 2.8-3.8 |
Mention any five importance of pH in our daily life?
Following are any five importance of first in our daily life
- Prevents tooth decay If the pH of your mouth drops below 5.5, teeth start to decay.
- Soil pH is an important factor. The ideal pH for plant growth is between 6.3 and 7.3.
- It helps in cleaning utensils.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is produced in the stomach when you eat food, or your stomach’s pH changes from 1 to 3, which helps digest the proteins in your food.
- Most of our body functions between a pH of 7 and 7.8.
Metals And Non-Metals Complete Chapter Notes With Examples
According to
Acid– An acid is a substance dissolved in water, release H+ ( Hydrogen Ions). The greater than number of H+ ions produce, the strong acid.
Example-
HCL + H2O —> H+ + Cl–
H2SO4 + H2O —-> 2H+ + SO42-
Hydrogen ions cannot exist freely in aqueous solution. They combine with H2O molecules to form H3O+ (Hydronium Ions).
Base (Alkali) – A Base is a substance which, dissolved in Water to produces OH– ions( Hydrogen Ions). The greater than number of OH– ions produce, the strong Base.
Example
NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻
KOH → K⁺ + OH⁻
- All base are not soluble in water
- water soluble bases are called alkalis.
- All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis.
Types of Acid Based On Strength
On the basis of strength, acids are two types
- Strong Acid- strong acid completely ionize in water to prodeuces large amount of H+ ions. (Example- HCL, H₂SO₄, HNO₃ etc.)
- Week Acid- Week acid the partially ionize in water and produces fewer H+ ions. ( Example- CH₃COOH, H₂CO₃, H3BO3 etc.)









1 comment